Sgr polygon kktg
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Are you struggling to create a normal distribution graph? This can be a daunting task for anyone, especially if you’re not a math expert. However, learning how to draw a normal distribution graph is essential for those in the fields of statistics, data science, and more. In this post, we’ll guide you step-by-step through the process of drawing a normal distribution graph, and provide you with tips and tricks to make the task easier.
Many people struggle with drawing a normal distribution graph because they don’t understand the underlying data. This can make it difficult to determine the shape of the curve or identify outliers. Additionally, determining the appropriate scale for the axes can be a challenge. However, by following the steps outlined below, you’ll be able to overcome these challenges and create a graph that accurately represents your data.
The target of how to draw a normal distribution graph
The first step in drawing a normal distribution graph is understanding what it represents. A normal distribution graph, also known as a bell curve, is a representation of a set of data that falls within a certain range. The graph is symmetric around the mean, with the majority of the data falling within one standard deviation of the mean.
To draw a normal distribution graph, you’ll need to follow these steps:
Step One: Collect and Analyze Your Data
The first step in drawing a normal distribution graph is collecting and analyzing your data. This will involve determining the mean and standard deviation of your data set. Once you have this information, you can begin to plot your data on the graph.
 Step Two: Determine the Appropriate Scale for the Axes
Step Two: Determine the Appropriate Scale for the Axes
The next step in drawing a normal distribution graph is determining the appropriate scale for the x and y axes. This will depend on the range of your data and the precision of your graph. In general, it’s best to use a scale that allows you to clearly see the distribution of your data without sacrificing accuracy.
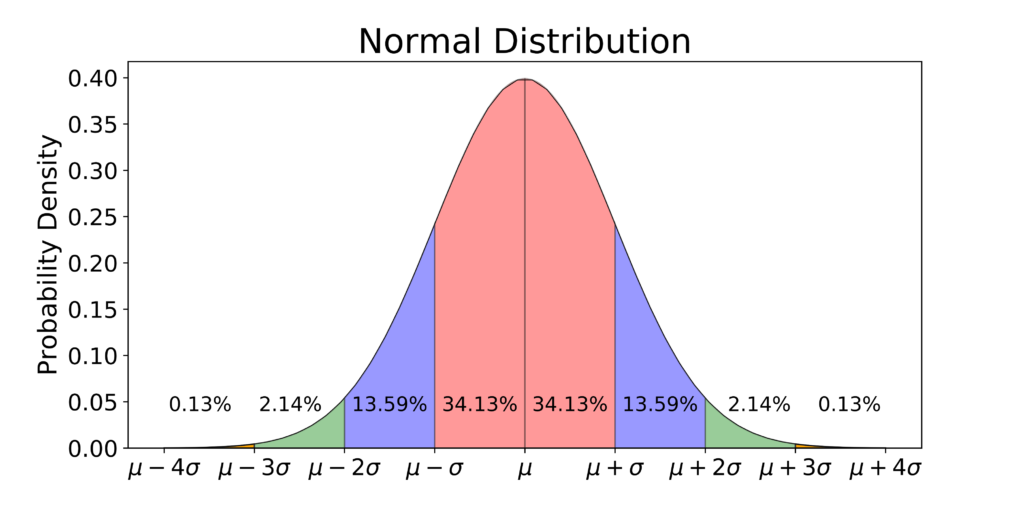 ### Step Three: Plot the Data
### Step Three: Plot the Data
The next step is to plot your data on the graph. You can use a spreadsheet program like Excel to do this, or you can plot the data by hand. If you’re using Excel, you’ll need to create a scatterplot and then add a trendline to the graph. The trendline should be a normal distribution curve.
Step Four: Interpret the Data
Once you’ve plotted your data, you can interpret the graph to gain insights into your data set. Pay attention to the mean and standard deviation, as well as the shape of the curve. If the data is skewed to one side, it may suggest that there are outliers in your data set. Additionally, if the curve is flatter than a typical normal distribution curve, it may suggest that the data has a larger standard deviation than expected.
Practical Tips for Drawing a Normal Distribution Graph
To make the process of drawing a normal distribution graph easier, we’ve compiled some practical tips:
- Use a spreadsheet program like Excel to create your graph
- Label your axes clearly and use units of measurement where necessary
- Use a scale that allows you to see the distribution of your data without sacrificing accuracy
- Double-check your calculations before plotting your data
Conclusion of how to draw a normal distribution graph
With these steps and tips, you should be able to confidently draw a normal distribution graph for your data set. Remember to collect and analyze your data, determine the appropriate scale for the axes, plot your data, and interpret the results. By following these steps, you’ll be able to gain valuable insights into your data and make informed decisions.
Question and Answer
Q: What are some common mistakes when drawing a normal distribution graph?
A: Some common mistakes include using the wrong scale for the axes, failing to label the axes clearly, and plotting inaccurate data.
Q: Can a normal distribution graph be skewed?
A: Yes, if the data set has outliers, the normal distribution curve may be skewed.
Q: What do the mean and standard deviation represent on a normal distribution graph?
A: The mean represents the average value of the data set, while the standard deviation represents how spread out the data is.
Q: How can I check if my data set follows a normal distribution?
A: You can check if your data set follows a normal distribution by creating a histogram of your data and checking if it’s bell-shaped.
Gallery
Normal Distribution: An Introductory Guide To PDF And CDF – Integrated

Photo Credit by: bing.com / distribution cdf introductory probability python
Normal Distribution - Explained Simply (part 2) - YouTube
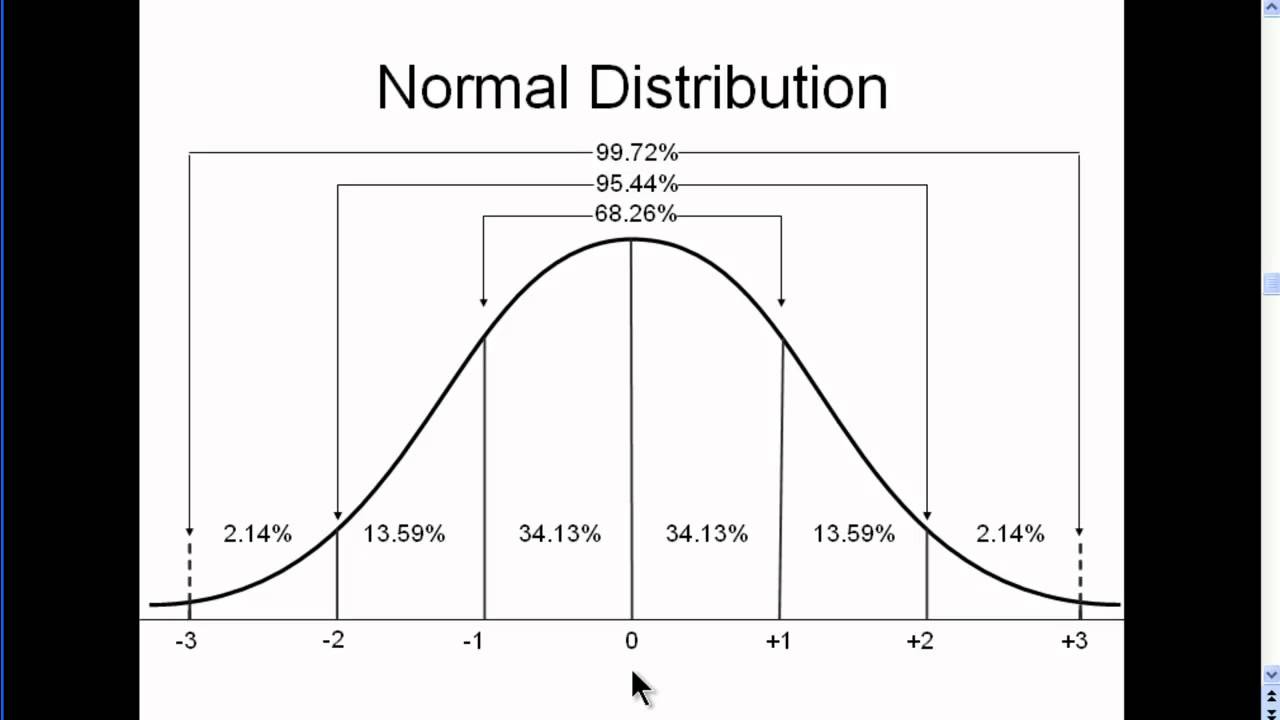
Photo Credit by: bing.com / distribution normal mean curve bell standard statistics deviation distributed normally explained probability part scores between simply sample work relationship figure
Draw A Normal Distribution Curve
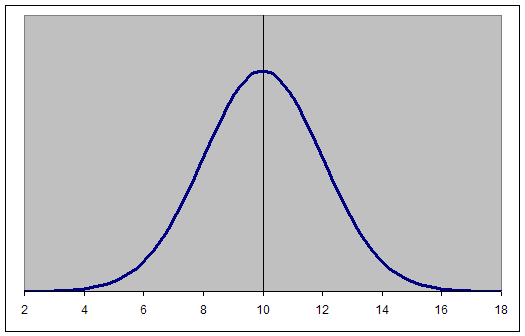
Photo Credit by: bing.com / normal curve distribution bell standard graph deviation excel gif other distributions statistics draw diabetes tushar years showing
Figure 15-14: Curve Drawing – SGR

Photo Credit by: bing.com / sgr polygon kktg
Understanding Z-Scores - MathBitsNotebook(A2 - CCSS Math)
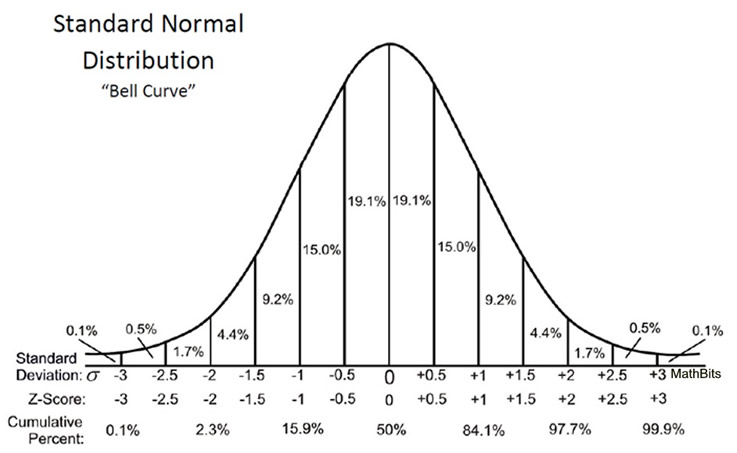
Photo Credit by: bing.com / standard distribution normal deviation table values score scores mean statistics negative curve deviations chart bell average value sd probability stat